Ir. Ikaputra, M.Eng., Ph.D., salah satu dosen Program Magister Program Studi Arsitektur DTAP UGM, menerbitkan artikel ilmiah berjudul “Three-Dimensional Digital Documentation for the Conservation of the Prambanan Temple Cluster Using Guided Multi-Sensor Techniques” di Jurnal Heritage, volume 8, issue 1 (2025). Karya ilmiah ini merupakan kolaborasi dengan berbagai pihak, yaitu bersama Anindya Sricandra Prasidya, S.T., M.Eng. (Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, Faculty of Earth Sciences and Technology ITB dan Department of Earth Technology, Vocational College UGM) selaku penulis pertama; Dr. Irwan Gumilar, S.T., M.Si. (Geodetic Science, Engineering, and Innovation Research Group, Faculty of Earth Sciences and Technology ITB); Prof. Dr. Irwan Meilano, S.T., M.Sc. (Spatial System and Cadastre Research Group, Faculty of Earth Sciences and Technology ITB); Ir. Rochmad Muryamto, M.Eng.Sc. (Department of Earth Technology, Vocational College UGM); dan Erlyna Nour Arrofiqoh, S.T., M.Eng. (Department of Earth Technology, Vocational College UGM).
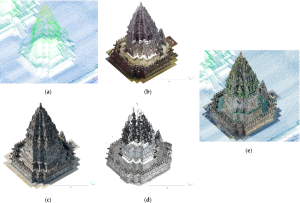
Publikasi ilmiah ini mendiskusikan hasil penelitian yang mengkaji pendokumentasian digital 3D untuk Candi Prambanan yang terletak di Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Candi Prambanan merupakan warisan budaya yang filosofis dan menunjukkan kemajuan pengetahuan dan keahlian konstruksi lokal pada masanya. Candi ini pun telah terdaftar sebagai Situs Warisan Dunia oleh UNESCO sejak tahun 1991. Tingginya nilai historis dan budaya yang dimiliki oleh Candi Prambanan perlu diimbangi dengan upaya konservasi yang baik. Terlebih lagi, pemeliharaan Candi Prambanan menghadapi berbagai tantangan, seperti bencana alam (gempa, erupsi), polusi, dan vandalisme. Dokumentasi digital 3D dapat menjadi salah satu upaya konservasi cagar budaya yang bermanfaat untuk evaluasi kerentanan struktur dan bahan penyusunan strategi konservasi. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengusulkan teknik dokumentasi aspek geometri pada towering concentric temple clusters (TCTCs) yang memiliki banyak dekorasi.
Abstrak publikasi ilmiah:
The Prambanan Temple cluster is a world heritage site that has significant value for humanity, a multiple zone cluster arrangement of highly ornamented towering temples, and a Hindu architectural pattern design. It lies near the Opak Fault, at the foothills of Mount Merapi, on an unstable ground layer, and is surrounded by human activities in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. The site’s vulnerability implies the necessity of 3D digital documentation for its conservation, but its complexity poses difficulties. This work aimed to address this challenge by introducing the utilization of architectural pattern design (APD) to guide multi-sensor line-ups for documentation. First, APDs were established from the literature to derive the associated multiple detail levels; then, multiple sensors and modes of light detection and ranging (Lidar) scanners and photogrammetry were utilized according to their detail requirements and, finally, point cloud data were processed, integrated, assessed, and validated by the proof of the existence of an APD. The internal and external qualities of each sensor result showed the millimeter- to centimeter-range root mean squared error, with the terrestrial laser scanner (TLS) having the best accuracy, followed by aerial close-range and terrestrial-mode photogrammetry and nadiral Lidar and photogrammetry. Two relative cloud distance analyses of every point cloud model to the reference model (TLS) returned the millimeter and centimeter ranges of the mean distance values. Furthermore, visually, every point cloud model from each sensor successfully complemented each other. Therefore, we can conclude that our approach is promising for complex heritage documentation. These results provide a solid foundation for future analyses, particularly in assessing structural vulnerabilities and informing conservation strategies.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage8010032
#SDG9
#SDG11
